What components make up a private cloud? The Primary Benefits of Private Clouds
The phrase “private cloud” is used to describe a cloud computing setup in which the hardware and software resources are made available to just one organisation or end-user. When it comes to functionality, a private cloud is not unlike from other types of cloud environments in that it uses physical components to provide users access to virtualized resources. Private cloud environments may be housed in an organization’s own data centre, but more and more businesses are turning to off-site providers for their private cloud infrastructure and services.
Potential adopters of cloud computing might easily be swept up in the buzz around the technology. While there are clear benefits to embracing cloud computing, it’s easy for potential adopters to be swept up in the hype, as is the case with many cutting-edge technology.
An updated call to arms
Before making the jump to the cloud, organisations need to give serious consideration to a variety of crucial issues. The following subjects will be covered in this resource:
- How a private cloud server really works.
- The differences between shared and encrypted cloud storage.
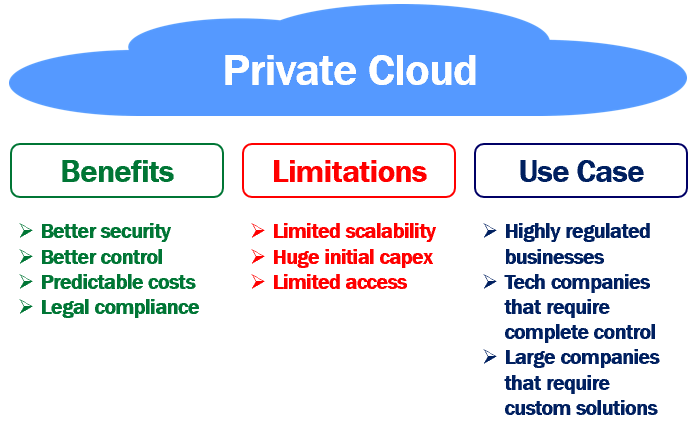
- The pros and cons of using a private cloud.
- Applications of private clouds.
In what ways might a personal cloud be utilised?
Understanding the inner workings of a private cloud calls for a refresher course on virtualization. Cloud computing relies heavily on virtualization since it is the backbone of the system. Virtualization is the process of creating digital representations of real-world items, such as computers, storage devices, servers, and networks, and hosting them in a remote data centre or “cloud.” In order to maximise productivity and save costs, several IT departments have begun to embrace the discipline of virtualization.
With the use of virtualization, many servers’ worth of resources may be combined into a single, secure, and isolated private cloud server. There is a strict one-user-per-session limit with this setting. This kind of cloud computing is not available to the general public but rather to a select group of companies, and it provides additional security by limiting access to only those companies. Typically, a month-to-month lease will be offered.
A private cloud server’s management responsibilities may rest with the legal owner of the server, although this is not necessarily the case. Private cloud servers, as previously mentioned, may be housed locally or hosted on the infrastructure of a cloud provider’s remote data centre.
Differences Between Public and Private Cloud Storage
Public clouds, in contrast to private ones, often allow several tenants to share a single cloud computing infrastructure with the general public. This kind of configuration is also known as a multi-tenant setting.
In a public cloud approach, the infrastructure and resources are supplied by a CSP or another vendor. Multiple tenants may share the same infrastructure under this setup. Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud are just a few of the top public cloud service providers. One of the biggest advantages of public cloud computing is that customers may buy these services on a pay-as-you-go basis. Organisations may adjust their resource allocation to match their growth, but doing so may lead to the buildup of hidden expenses over time.
Conclusion
Therefore, although the public cloud may be able to give more scalability as the company’s needs grow, the private cloud may provide more privacy and be compatible with more programmes.






